
With 7.3% CAGR, The "Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) Market" size is expected to grow from 194.2 million USD In 2020, to reach 296.5 Million USD by 2026. We can see a large potential market for this cellular ingredient in the dietary supplements field. Meanwhile, we’re encountering many challenges such as strict regulations in many countries, lacking innovative formulations for novel fields etc.
New study
On 5th May 2022, Frontier in Aging, an authoritative international journal on aging mechanisms, published one NMN human clinical trial report showing good efficacy and safety in middle aged and older adults. The 66-subject trial built on evidence that NMN has no acute and sub-chronic toxicity and is not mutagenic and clastogenic.
In this analysis, compared with the placebo group, the blood cellular NAD(H), 6 minute walking endurance test, SF-36 in the NMN group showed a trend of improvement. As an endogenous compound, NMN cannot be used as a drug to rejuvenate the human body in a short time, but the experiment has shown the improvement trend of NMN.

Highlights of this trial
NMN is a precursor to a vital molecule for energy production and metabolic health called nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+). Some human studies were trying to evaluate the efficacy of NMN to increase NAD(H) and test NMN metabolites. But the results cannot be shown visually.
In this report, at the end of the study (day 60), the NAD(H) levels were increased further by 38% from baseline in the NMN group, compared to a 14.3% rise in the placebo group.
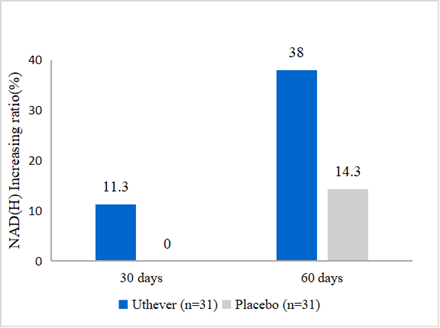
Figure1
NMN is widely applied in anti-aging supplements, but hardly found in sports nutrition. IHP tested the walk endurance of NMN for the first time. The walking endurance increased by 6.5% in the NMN group and 3.9% in the placebo group on day 60 of the treatment. From this analysis, it was clear that the placebo effect was evident until day 30, but after that, the NMN group showed further improvement in walking endurance, whereas the placebo group remained at the same level.
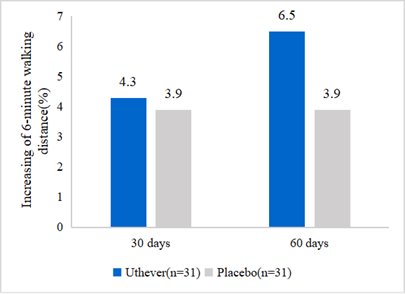
Figure2
IHP used the SF 36 questionnaire to demonstrate the rise of subjects’ health scores. At day 60, the NMN group showed a rise of 6.5%, whereas the placebo group was raised by 3.4%. The increase in scores in the NMN group was almost double the increase seen in the placebo group.
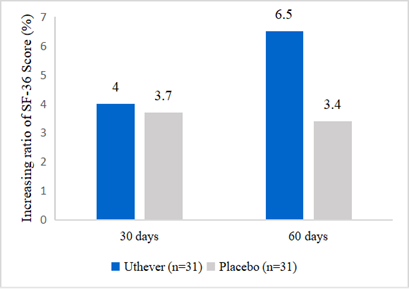
Figure 3
The little changes of HOMA-IR and fasting insulin and fasting glucose in the NMN group indicated the more stability of glucose and serum insulin.
At the end of the study, the mean HOMA IR index showed a rise of 0.6% among the NMN group and a rise of 30.6% among the placebo group from baseline. Mean glucose (sugar) fasting showed a fall of 4.0% among the NMN group and rise of 6.5% among the placebo group from baseline. Mean serum insulin fasting showed a fall of 1.9% among the NMN group versus a rise of 26.2% among the placebo group from baseline.
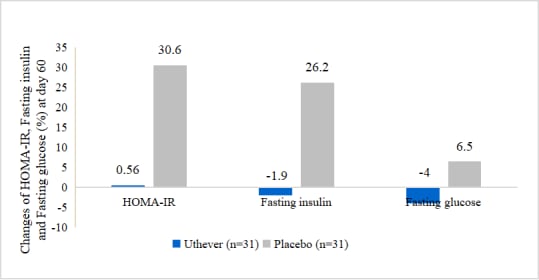
Figure 4
Copyright © 2002-2024 Mageleafhealth ADDRESS:12560 Bridgeport Rd Unit 260 Suite 105 Richmond; BC; Canada